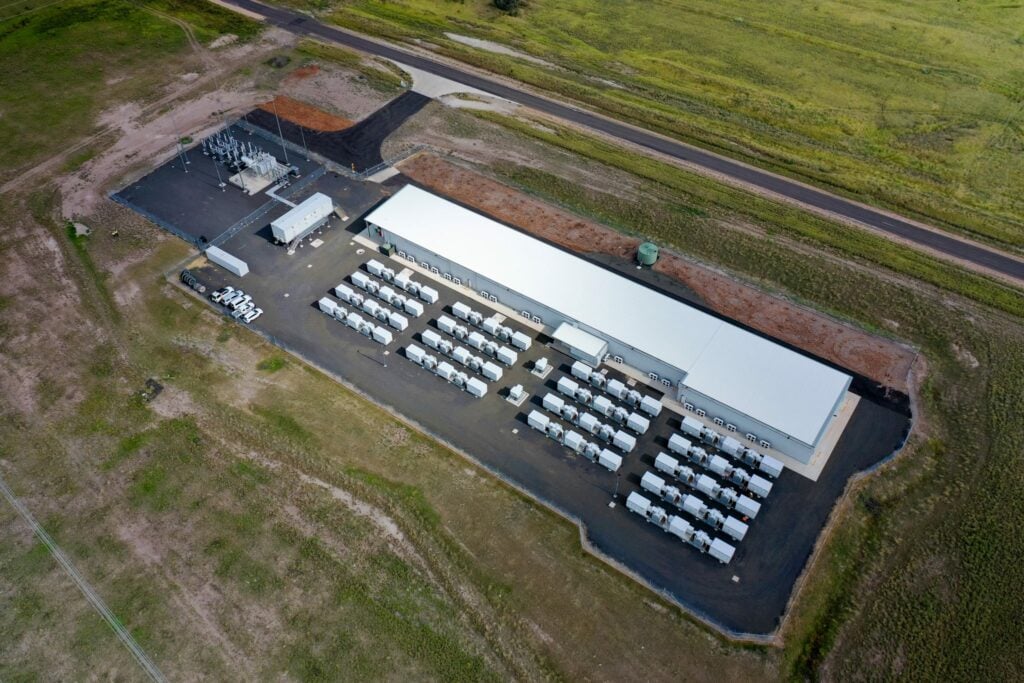
The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) has found that battery energy storage systems (BESS) are the most reliable clean energy technology in the National Electricity Market (NEM).
According to AEMO’s new 2025 Electricity Statement of Opportunities report, battery energy storage systems demonstrate the highest reliability, with approximately 70% of the NEM’s fleet having experienced unplanned outage rates of only 0-5%.
It adds that longer-duration storage, defined as 4-hours or more, is more effective at reducing reliability risks than shorter-duration storage. This is because in 2030-31, expected USE in South Australia is forecast to exceed the reliability standard, with some shortfall events lasting more than four hours.
In such conditions, AEMO said 2-hour battery storage systems are typically exhausted early, providing no reliability benefits for later hours of the forecast USE event. By contrast, longer duration storage can sustain output over a larger portion or even across the full duration of these USE events.
This article requires Premium SubscriptionBasic (FREE) Subscription
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
Already a subscriber? Sign In
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
Already a subscriber? Sign In
Energy storage deployment to tackle grid reliability gaps
Energy storage continues to emerge as a critical component of Australia’s energy transition strategy. AEMO’s report reveals various storage durations and their effectiveness in meeting reliability standards, providing crucial insights for developers and policymakers.
Indeed, several different technology combinations in South Australia could be sought to help reduce expected unserved energy (USE) and meet reliability standards by 2030-31.
For instance, AEMO states that 820MW of 2-hour storage would be required to reduce expected USE to meet the reliability standard. In contrast, less than half that capacity is needed if the storage has a duration of 4-hours or more – specifically, 365MW of 4-hour storage would suffice.
The report also demonstrates that longer-duration storage options could provide increasingly efficient solutions: 6-hour duration storage, for example, would require 320MW. In contrast, 8-hour storage would need approximately 315MW to achieve the same reliability outcomes.
According to AEMO, hybrid configurations show even greater efficiency gains. When wind is combined with 4-hour duration energy storage, the requirement drops to 295MW of storage co-located with 590MW of wind generation.
Similarly, solar PV combined with 4-hour storage would require 285MW of energy storage alongside 570MW of solar. The most efficient configuration examined involves a combination of wind, solar and 4-hour storage, requiring 280MW of storage, 555MW of wind and 140MW of solar.
To read the full article, please visit our sister site PV Tech.
Our publisher Solar Media will be hosting the Energy Storage Summit Australia 2025 in Sydney from 18-19 March. You can get 20% off your ticket by following the link here.
Read Next
Several new community batteries have been launched in Victoria and Queensland, Australia, to soak up distributed solar PV.
State-owned utility Western Power has commissioned five new community batteries in Perth suburbs as part of a federally funded initiative in Western Australia.
ACE Power has confirmed the sale of the 103MW/206MWh Kerang grid-forming BESS in the Loddon Valley region of Victoria, Australia.
“It’s the most powerful BESS in the world,” Nick Carter of Akaysha Energy, tells ESN Premium after switching on the Waratah Super Battery in New South Wales, Australia.
Most Popular
Email Newsletter
This site is operated by a business or businesses owned by Informa PLC and all copyright resides with them. Informa PLC’s registered office is 5 Howick Place, London SW1P 1WG. Registered in England and Wales. Number 8860726.